Modern humans began the first steps to what we might call culture some 50,000 years ago, 150,000 years after appearing in the fossil record. What changed?
A new paper in Current Anthropology argues that more feminine faces and gentler personalities were the result of less testosterone. People got nicer. The evidence is in the shape of more than 1,400 ancient and modern skulls and the conclusion is that human society advanced when people started being nicer to each other, which entails having a little less testosterone in action.
Heavy brows were so 100,000 B.C., rounder heads were in, and those changes could be linked to testosterone levels acting on the skeleton, according to Duke University anthropologist Steven Churchill.
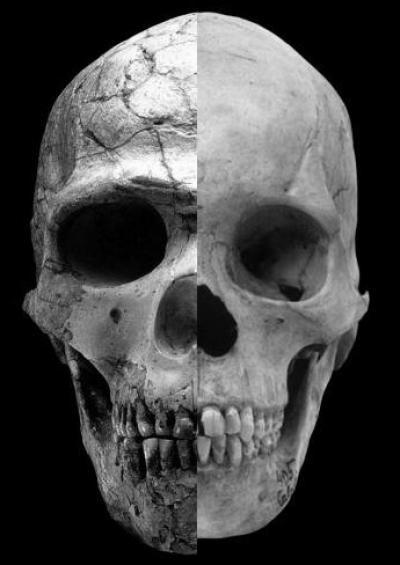
A composite image shows the facial differences between an ancient modern human with heavy brows and a large upper face and the more recent modern human who has rounder features and a much less prominent brow. The prominence of these features can be directly traced to the influence of the hormone testosterone. Credit: Robert Cieri, University of Utah
What would settle the issue is if they knew whether these humans had less testosterone in circulation, or fewer receptors for the hormone.
There is a lot of theories about why, after 150,000 years of existence, humans suddenly leapt forward in technology. Around 50,000 years ago, there is widespread evidence of producing bone and antler tools, heat-treated and flaked flint, projectile weapons, grindstones, fishing and birding equipment and a command of fire. Was this driven by a brain mutation, cooked foods, the advent of language or just population density?
The paper argues that living together and cooperating put a premium on agreeableness and lowered aggression and that, in turn, led to changed faces and more cultural exchange.
The research team also included Duke animal cognition researchers Brian Hare and Jingzhi Tan, who say this argument is in line with what has been established in non-human species.
In a classic study of Siberian foxes, animals that were less wary and less aggressive toward humans took on a different, more juvenile appearance and behavior after several generations of selective breeding.
"If we're seeing a process that leads to these changes in other animals, it might help explain who we are and how we got to be this way," said Hare, who also studies differences between our closest ape relatives -- aggressive chimpanzees and mellow, free-loving bonobos.
Those two apes develop differently, Hare said, and they respond to social stress differently. Chimpanzee males experience a strong rise in testosterone during puberty, but bonobos do not. When stressed, the bonobos don't produce more testosterone, as chimps do, but they do produce more cortisol, the stress hormone.
Their social interactions are profoundly different and, relevant to this finding, their faces are different, too. "It's very hard to find a brow-ridge in a bonobo," Hare said.
Cieri compared the brow ridge, facial shape and interior volume of 13 modern human skulls older than 80,000 years, 41 skulls from 10,000 to 38,000 years ago, and a global sample of 1,367 20th century skulls from 30 different ethnic populations.
The trend that emerged was toward a reduction in the brow ridge and a shortening of the upper face, traits which generally reflect a reduction in the action of testosterone.

For a senior honors thesis at Duke, Robert Cieri used facial measurements from more than 1,400 ancient and modern human skulls. Some of the measurements he made himself; others were taken from previous studies. Credit: Robert Cieri, University of Utah
"If prehistoric people began living closer together and passing down new technologies, they'd have to be tolerant of each other," Cieri said. "The key to our success is the ability to cooperate and get along and learn from one another."






Comments