 Could Niacin Be Added To Glioblastoma Treatment?
Could Niacin Be Added To Glioblastoma Treatment?Glioblastoma, a deadly brain cancer, is treated with surgery to remove as much of the tumor as...
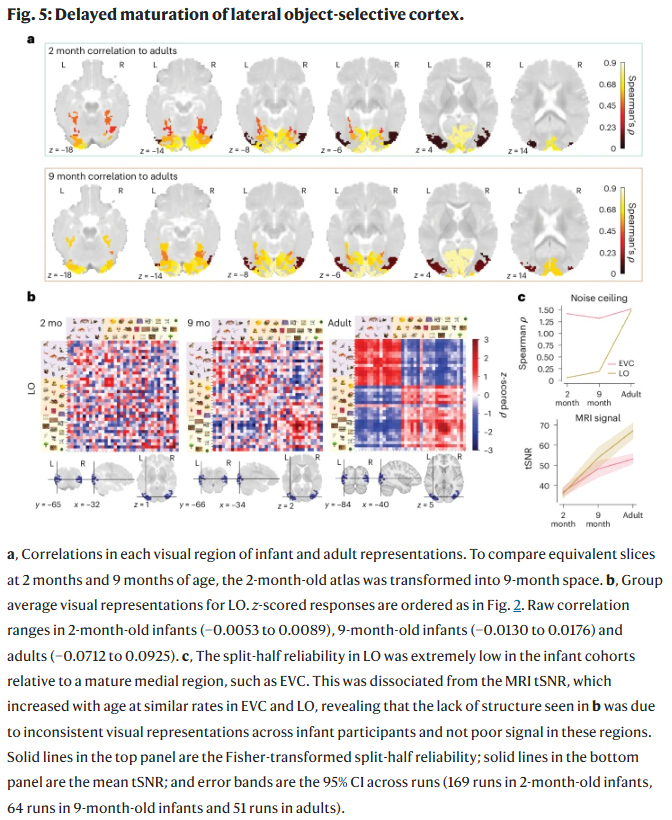 At 2 Months, Babies Can Categorize Objects
At 2 Months, Babies Can Categorize ObjectsAt two months of age, infants lack language and fine motor control but their minds may be understanding...
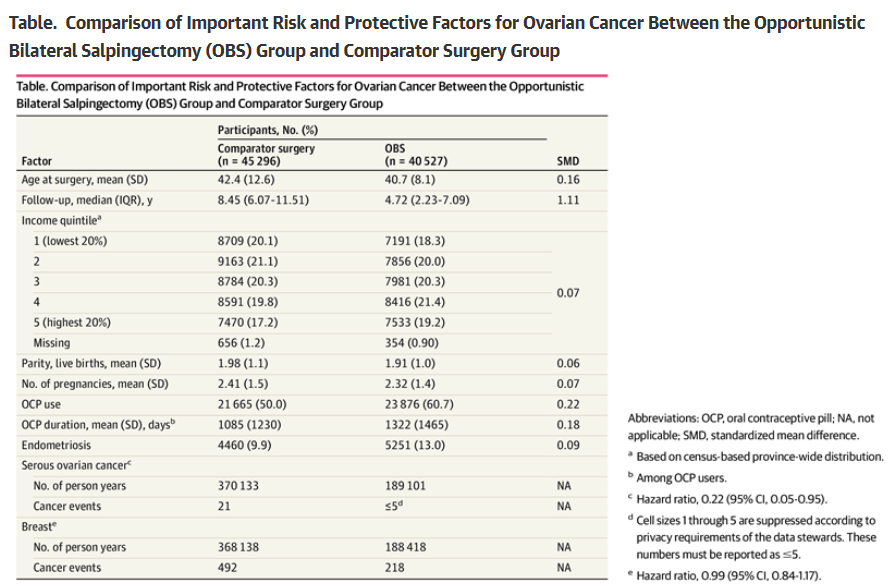 Opportunistic Salpingectomy Reduces Ovarian Cancer Risk By 78%
Opportunistic Salpingectomy Reduces Ovarian Cancer Risk By 78%Opportunistic salpingectomy, proactively removing a person’s fallopian tubes when they are already...
 Environmental Activists Hate CRISPR - And They're Dooming People With HIV
Environmental Activists Hate CRISPR - And They're Dooming People With HIVExisting treatments control HIV but the immune system does not revert to normal. They is why people...