The search for clean, green sustainable energy sources marches on. While some studies note that solar and wind energy could be viable by 2025, if they could bypass environmental lawsuits, hydrogen and nuclear are rushing to fill the gaps.
Plants are not wrong, artificial photosynthesis, such as bionic leaves that produce energy-dense fuels from nothing more than sunlight, water and atmosphere-warming carbon dioxide, represent an ideal alternative to fossil fuels. Earth receives more energy in one hour's worth of sunlight than all of humanity uses in an entire year. Through the process of photosynthesis, green plants harness solar energy to split molecules of water into oxygen, hydrogen ions (protons) and free electrons. The oxygen is released as waste and the protons and electrons are used to convert carbon dioxide into the carbohydrate sugars that plants use for energy. Scientists aim to mimic the concept but improve upon the actual process.
A major step toward meeting at least one of these challenges has been achieved by researchers with the U.S. Department of Energy (DOE)'s Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory (Berkeley Lab) working at the Joint Center for Artificial Photosynthesis (JCAP).
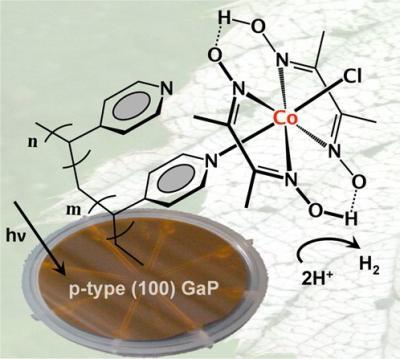
Grafting molecular cobalt-containing hydrogen production catalysts to a visible-light-absorbing semiconductor exploits the UV-induced immobilization chemistry of vinylpyridine to p-type (100) gallium phosphide (GaP). Image from Gary Moore, Berkeley Lab/JCAP
"We've developed a method by which molecular hydrogen-producing catalysts can be interfaced with a semiconductor that absorbs visible light," says Gary Moore, a chemist with Berkeley Lab's Physical Biosciences Division and principal investigator for JCAP. "Our experimental results indicate that the catalyst and the light-absorber are interfaced structurally as well as functionally."
JCAP, which has a northern branch in Berkeley and a southern branch on the campus of the California Institute of Technology (Caltech), was established in 2010 by DOE as an Energy Innovation Hub. Operated as a partnership between Caltech and Berkeley Lab, JCAP is the largest research program in the United States dedicated to developing an artificial solar-fuel technology. While artificial photosynthesis can be used to generate electricity, fuels can be a more effective means of storing and transporting energy. The goal is an artificial photosynthesis system that's at least 10 times more efficient than natural photosynthesis.
To this end, once photoanodes have used solar energy to split water molecules, JCAP scientists need high performance semiconductor photocathodes that can use solar energy to catalyze fuel production. In previous efforts to produce hydrogen fuel, catalysts have been immobilized on non-photoactive substrates. This approach requires the application of an external electrical potential to generate hydrogen. Moore and his colleagues have combined these steps into a single material.
"In coupling the absorption of visible light with the production of hydrogen in one material, we can generate a fuel simply by illuminating our photocathode," Moore says. "No external electrochemical forward biasing is required."
The new JCAP photocathode construct consists of the semiconductor gallium phosphide and a molecular cobalt-containing hydrogen production catalyst from the cobaloxime class of compounds. As an absorber of visible light, gallium phosphide can make use of a greater number of available solar photons than semiconductors that absorb ultraviolet light, which means it is capable of producing significantly higher photocurrents and rates of fuel production. However, gallium phosphide can be notoriously unstable during photoelectrochemical operations.
Moore and his colleagues found that coating the surface of gallium phosphide with a film of the polymer vinylpyridine alleviates the instability problem, and if the vinylpyridine is then chemically treated with the cobaloxime catalyst, hydrogen production is significantly boosted.
"The modular aspect of our method allows independent modification of the light-absorber, linking material and catalyst, which means it can be adapted for use with other catalysts tethered over structured photocathodes as new materials and discoveries emerge," Moore says. "This could allow us, for example, to replace the precious metal catalysts currently used in many solar-fuel generator prototypes with catalysts made from Earth-abundant elements."
Despite its promising electronic properties, gallium phosphide features a mid-sized optical band gap which ultimately limits the total fraction of solar photons available for absorption. Moore and his colleagues are now investigating semiconductors that cover a broader range of the solar spectrum, and catalysts that operate faster at lower electrical potentials. They also plan to investigate molecular catalysts for carbon dioxide reduction.
"We look forward to adapting our method to incorporate materials with improved properties for converting sunlight to fuel," Moore says. "We believe our method provides researchers at JCAP and elsewhere with an important tool for developing integrated photocathode materials that can be used in future solar-fuel generators as well as other technologies capable of reducing net carbon dioxide emissions."






Comments