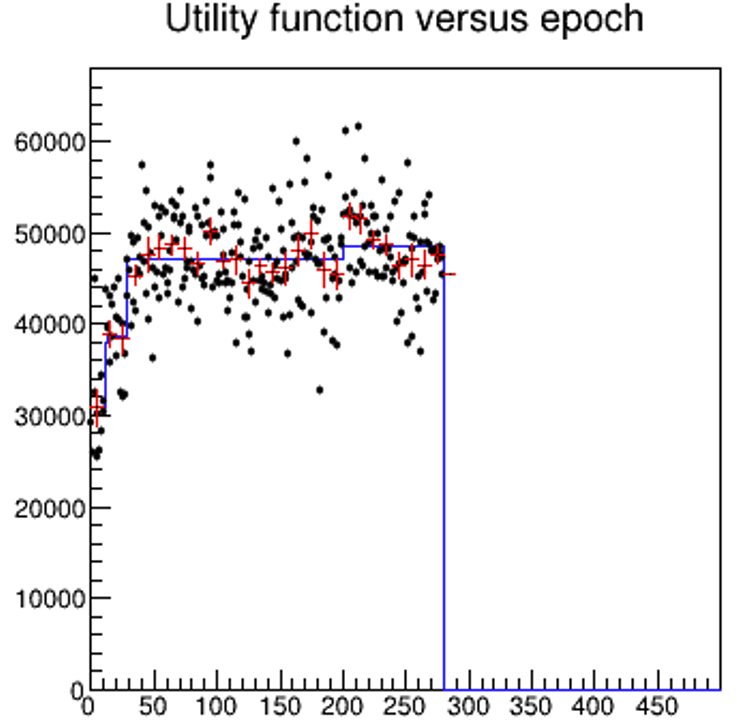
These days I am putting the finishing touches on a hybrid algorithm that optimizes a system (a gamma-ray observatory) by combining reinforcement-learning with gradient descent. Although I published an optimization strategy for that application already, I am going back to it to demonstrate a case where the simultaneous optimization of hardware and software is necessary, for a paper on co-design I am writing with several colleagues.
In the course of the software development, I ran into a simple but still interesting statistical issue I had not paid attention to until now. So I thought I could share it with you here.
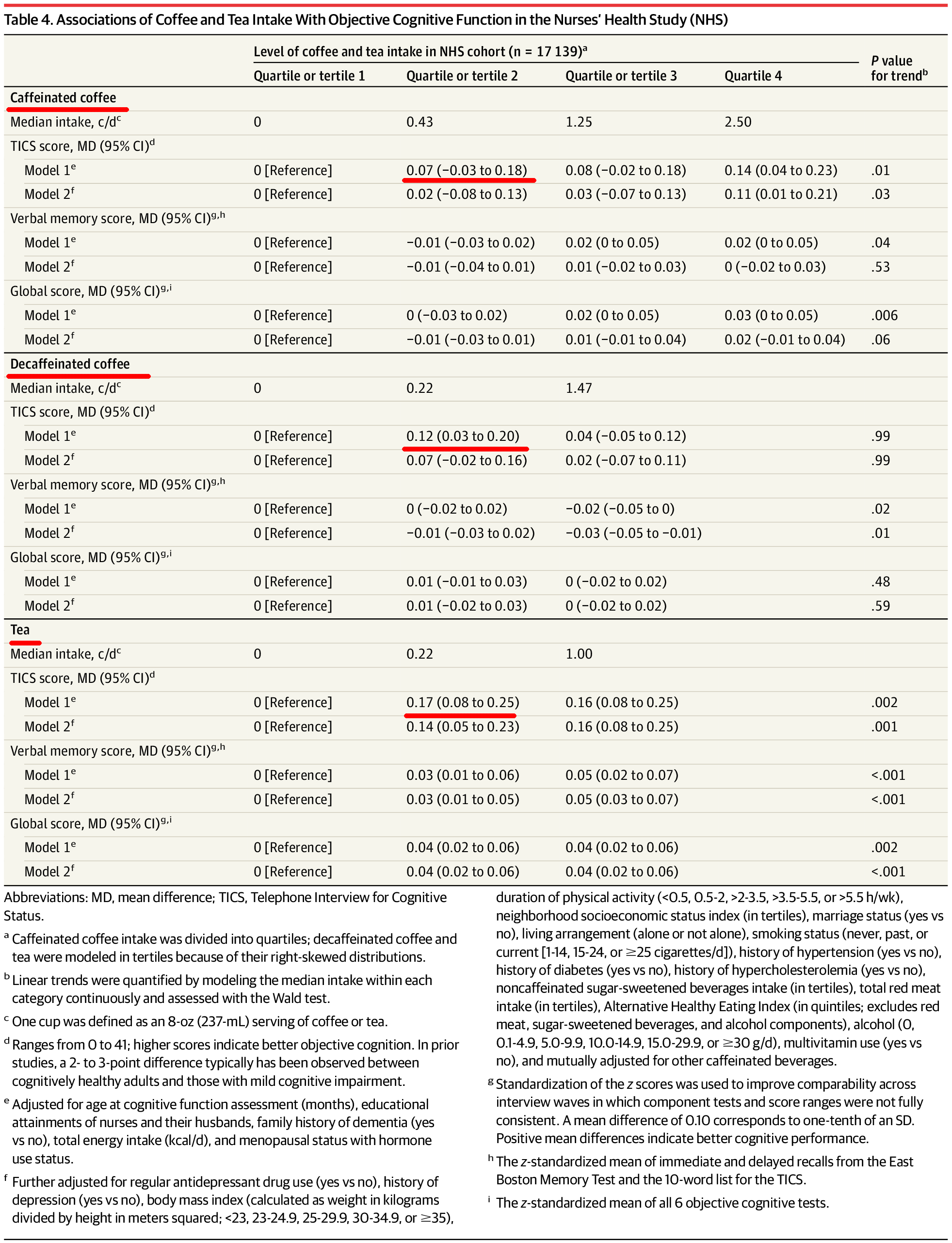
A new paper says that players where a few superstars get the money leads to less cooperation and poor team performance. The authors say this salary compression is why teams won fewer games.
The authors also suggest that companies should strive for more equity in pay, to increase synchronized effort. Because individual effort by key people isn't enough.
They may have a point. The U.S. Army pays everyone, good or bad, the same, and it is the best in the world. But current military and veterans will laugh if a humanities academic suggests it it more efficient or cooperative because of equal pay. Instead, they will tell the stories of all the people their unit had to carry, because it's not a meritocracy and reductions only happen at promotion tiers.
In 2026, it is easy to feel intellectually knocked around by all of the health claims you read, and all claiming to be supported by science. Weedkillers causing cancer, food coloring causing diabetes, vaccines causing autism, and ultra-processed foods causing everything else are part of a Vast R̶i̶g̶h̶t̶-̶ Left-Wing Conspiracy to make us compliant and Evil Corporations rich.
Thinking about the new Trump administration in 2024, Republicans transforming into the 1990s Democratic party - except they haven't banned nuclear power again yet - was not on anyone's Cultural Bingo card.(1)
In late January 2026, New York Magazine published a striking piece of cultural reporting: wellness clinics, influencer funnels, and WhatsApp “consultants” selling the dream of brighter skin, faster fat loss, and cleaner energy—often via compounds framed as “peptides,” sometimes as other “cellular” molecules bundled alongside them.
Olympians Chloe Kim and Eileen Gu are both Americans but have Asian descent. Yet Kim competed for her country in 2018 while Gu chose to instead compete for Communist China, which does not allow dual citizenship
yet actively recruits foreign athletes to be on their Olympic team even if they have no Chinese ancestry at all.
Humanities academics say American media have been hard on Gu because she chose to compete for China, whereas Kim was celebrated. Maybe. She'd have lost her passport if she had done it to the CCP. The authors suggest it is because Gu's father is white.
Glioblastoma, a deadly brain cancer, is treated with surgery to remove as much of the tumor as possible and then radiation and chemotherapy.
Like all cancer, that may not be the end of it. Sometimes, the aggressive cancer returns. A recent study sought to find out if high doses of vitamin B3 or niacin could help, by rejuvenating compromised immune cells to kill tumor cells, the way it had with mice. The researchers found that while glioblastoma suppresses the immune system, niacin in mice gave immune cells a boost so they could continue to attack and destroy cancer cells.
Culture wars are as eternal as shooting wars, and that means there will always be war profiteers. Misandry and Manosphere poles get media attention when opening new fronts and those mean products appealing to both and then demography papers will follow.
Strange how time goes by. And strange I would say that, since I know time does not flow, it is just our perception of one of the spacetime coordinates of our block universe...
The thing is, on February 5 I will turn 60. An important date for anybody - I could say a milestone. First of all, let me say that we give for granted all the days of our life we got to live, but in truth we did not know it from the start we would make it far. I do feel rather young still, but I am very well aware that there are heaps of ways I could have ended my life earlier. Accidents, but also naturally occurring sickness.
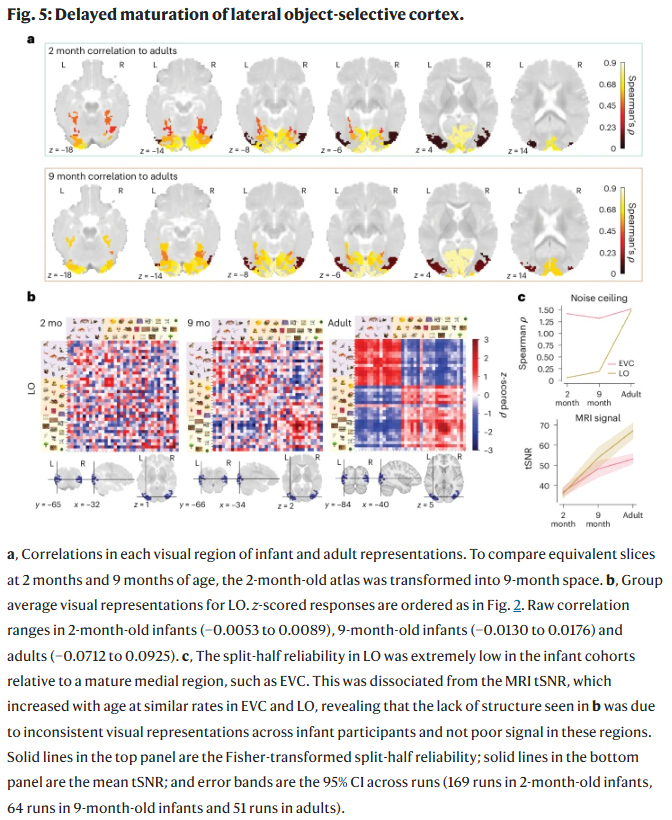
At two months of age, infants lack language and fine motor control but their minds may be understanding how things look and figuring out to which category they belong, which would push back earlier beliefs about the foundations of visual cognition.
A new study recruited 130 two-month-old infants who were placed on a beanbag chair wearing sound-canceling headphones, while shown bright, colorful images which kept them engaged for 15-20 minutes. The team used functional MRI (fMRI) to measure changes in brain activity in response to pictures representing 12 common visual categories such as cat, bird, rubber duck, shopping cart and tree.
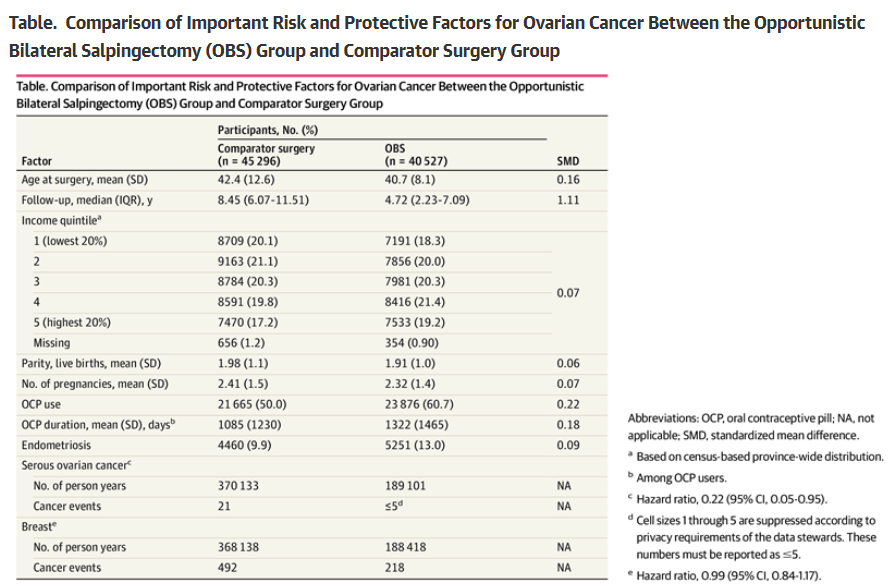
Opportunistic salpingectomy, proactively removing a person’s fallopian tubes when they are already undergoing a gyecological surgery such as hysterectomy or tubal ligation, may be a way to reduce ovarian cancer risk. Most ovarian cancers originate in the fallopian tubes rather than the ovaries and ovarian cancer is the most lethal gynecological cancer.