The 10th congress of the USERN organization was held on November 8-10 in Campinas, Brazil. Some time has gone by, so it is due time for me to report on the event. I could not attend in person for a cause of force majeure, but I was connected via zoom, and I also delivered two recorded speeches plus one talk in one of the parallel "virtual session" that were run via zoom in the evenings (CET) after the in-person program of the day was over.
I am moving some baby steps in the direction of Reinforcement Learning (RL) these days. In machine learning, RL is a well-established and very promising avenue for the development of artificial intelligence, and the field is in rapid development. Unfortunately I have been left behind, as I never really needed to fiddle with those techniques for my research. Until recently.
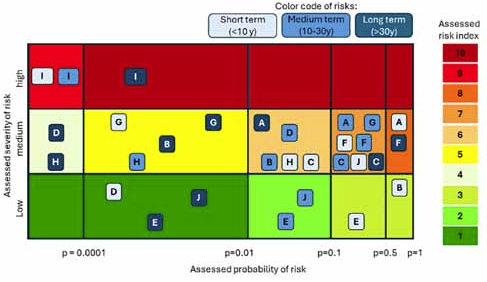
Truth is under attack. It has always been, of course, because truth has always been a mortal enemy for those who attempt to seize or keep power in their hands. But the amplification of the phenomenon by today's information technology is extremely worrisome. AI today can generate fake videos and images that even experts have trouble flagging as such. This, combined with the different news value and propagation potential of false information with respect to typically less attention-grabbing true facts has created an explosive situation. What to do?
Today is November 1st, the day dedicated to the dead, and I am in northern Sweden where daylight is scarce this time of the year. The two things conjure to arise thoughts of a darkish nature.
 [Above, a lousy picture taken this evening in a cemetery in Gammelstad, close to Lulea, in Norrbotten, Sweden. Sorry for the bad quality... Yet the landscape with all those small lights was really inspiring.]
[Above, a lousy picture taken this evening in a cemetery in Gammelstad, close to Lulea, in Norrbotten, Sweden. Sorry for the bad quality... Yet the landscape with all those small lights was really inspiring.]
Having interacted for a few months with ChatGPT 5 now, both for work-related problems and for private / self-learning tasks, I feel I might share some thoughts here on what these large models can tell us about our own thought processes.
The sentence above is basically giving away my bottomline from square one, but I suppose I can elaborate a bit more on the concept. LLMs have revolutionized a wide range of information-processing tasks in just three or four years. Looking back, the only comparable breakthrough I can recall is the advent of internet search engines in the early 1990s. But as exciting and awesome this breakthrough is, it inspires me still more to ponder on how this is even possible. Let me unpack this.
With this post I would like to present a short update of my personal life to the few readers who are interested in that topic. You know, when I started writing online (over 20 years ago!), blogs used to contain a much more personal, sometimes introspective, description of the owner's private life and actions. Since long, they have been substituted by much more agile, quick-to-consume videos. But the old-fashioned bloggers who stuck with that medium continue to have a life - albeit certainly a less glamorous one than that of today's influencers; so some reporting of personal affairs is not out of place here.
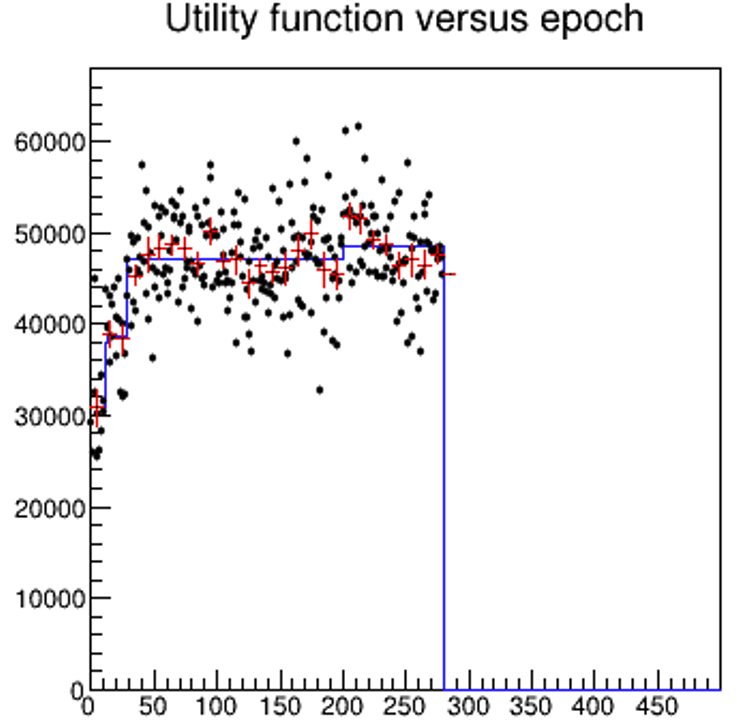 The Strange Case Of The Monotonous Running Average
The Strange Case Of The Monotonous Running Average Turning 60
Turning 60 On The Illusion Of Time And The Strange Economy Of Existence
On The Illusion Of Time And The Strange Economy Of Existence RIP - Hans Jensen
RIP - Hans Jensen